Moths with fruit or seed eating larvae
While most moth larvae feed on foliage, some specialise in eating ripening fruits or developing seeds, and can be a nuisance in the garden.
Species in Britain and Ireland
The species most likely to be seen in gardens are codling moth, Cydia pomonella; plum moth, Grapholita funebrana; and pea moth, Cydia nigricana. There are other moths with larvae that feed on dry stored seeds, such as cereal grains, but they are not garden insects.
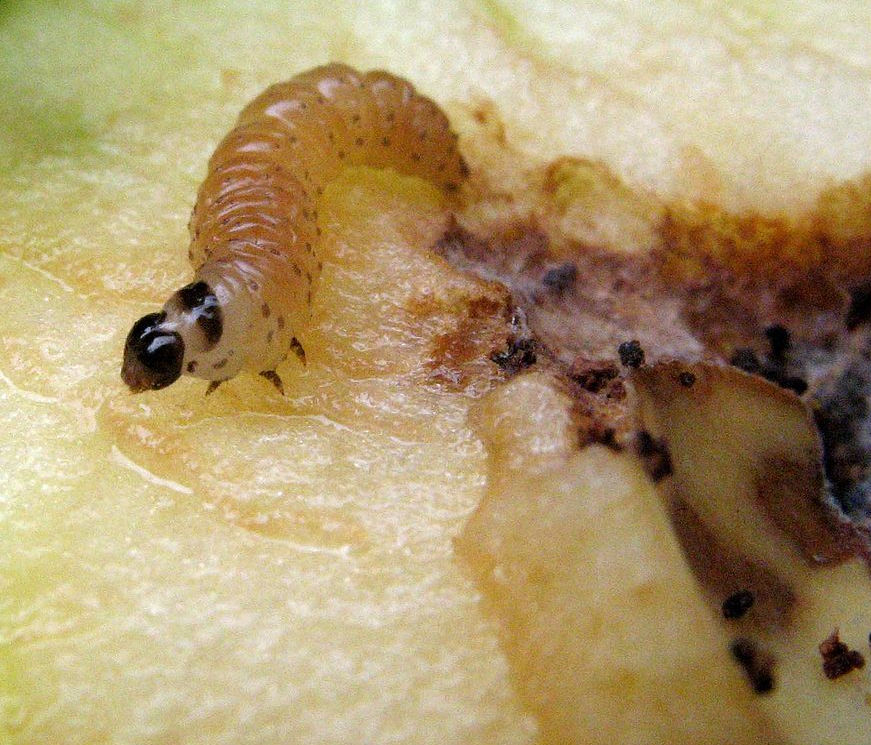
The codling moth Cydia pomonella commonly infests the fruit of apples. It is said that the only thing worse than finding a codling moth larva in your bitten apple, is finding half a caterpillar in the same situation.

Biology
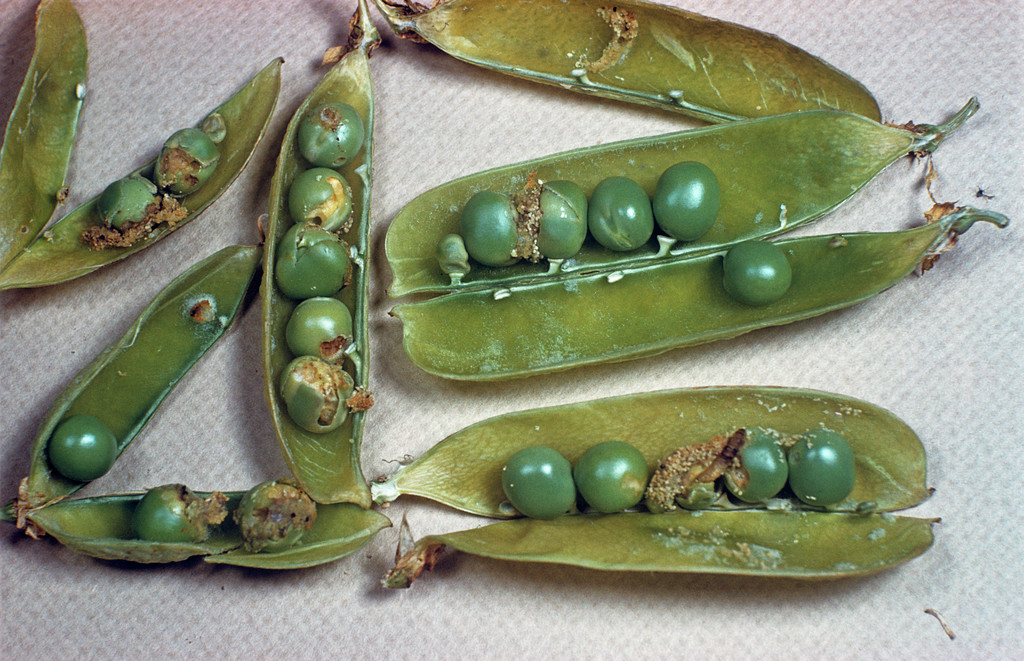
The larvae of codling moth feed in the core of apples and pear fruits – they are the cause in late summer of maggoty apples. Plum moth larvae develop in the fruits of plums, damson and greengages. Pea moth larvae develop inside pea pods, where they eat the green pea seeds.
Life cycle
Codling moth, plum moth and pea moth normally have one generation during the summer in Britain but in years with long hot summers, codling moth can produce a second generation. The moths lay eggs in early summer on the developing fruits of apples, pears or plums and pea pods. After hatching the young larvae tunnel into the fruits or pea pods, where they remain until they have completed their feeding, when they leave. Codling moth and plum moth overwinter as larvae in silk cocoons under loose bark or in leaf litter before pupating in spring. Fully fed pea moth larvae similarly overwinter in the soil and pupate in spring.
Role of fruit/seed-eating moths in gardens
The caterpillars of codling moth, plum moth and pea moth can in some years damage a large proportion of the potential crop, making them some of the less desirable components of a garden’s biodiversity.
Other sources of information
Website
Website of UK Moths
RHS advice on codling moth
RHS advice on plum moth
RHS advice on pea moth
Books
Sterling, P., Parsons, M. and Lewington R. (2018) Field Guide to the Micro-moths of Great Britain and Ireland. British Wildlife Publications
Page drafted by Andrew Halstead, reviewed by Andrew Salisbury, edited by Steve Head
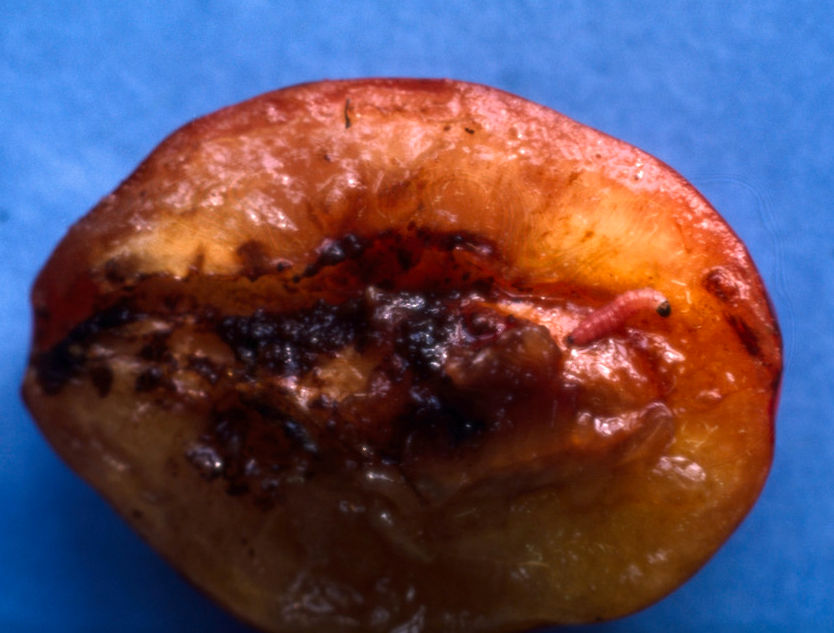

Caterpillar of codling moth, Cydia pomonella Plum moth, Grapholita funebrana in core of a plum
Pea moth Cydia nigricana larvae and droppings inside opened pea pods.
- Home
- Garden Wildlife
- Insects
- Lepidoptera
- Fruit-eating moths
Moths with fruit or seed eating larvae
While most moth larvae feed on foliage, some specialise in eating ripening fruits or developing seeds, and can be a nuisance in the garden.
Species in Britain and Ireland
The species most likely to be seen in gardens are codling moth, Cydia pomonella; plum moth, Grapholita funebrana; and pea moth, Cydia nigricana. There are other moths with larvae that feed on dry stored seeds, such as cereal grains, but they are not garden insects.
The codling moth Cydia pomonella commonly infests the fruit of apples. It is said that the only thing worse than finding a codling moth larva in your bitten apple, is finding half a caterpillar in the same situation.


Pea moth Cydia nigricana larvae and droppings inside opened pea pods.
Biology
The larvae of codling moth feed in the core of apples and pear fruits – they are the cause in late summer of maggoty apples. Plum moth larvae develop in the fruits of plums, damson and greengages. Pea moth larvae develop inside pea pods, where they eat the green pea seeds.
Life cycle
Codling moth, plum moth and pea moth normally have one generation during the summer in Britain but in years with long hot summers, codling moth can produce a second generation. The moths lay eggs in early summer on the developing fruits of apples, pears or plums and pea pods. After hatching the young larvae tunnel into the fruits or pea pods, where they remain until they have completed their feeding, when they leave. Codling moth and plum moth overwinter as larvae in silk cocoons under loose bark or in leaf litter before pupating in spring. Fully fed pea moth larvae similarly overwinter in the soil and pupate in spring.
Role of fruit/seed-eating moths in gardens
The caterpillars of codling moth, plum moth and pea moth can in some years damage a large proportion of the potential crop, making them some of the less desirable components of a garden’s biodiversity.
Other sources of information
Website
Website of UK Moths
Books
Sterling, P., Parsons, M. and Lewington R. (2018) Field Guide to the Micro-moths of Great Britain and Ireland. British Wildlife Publications
Page drafted by Andrew Halstead, reviewed by Andrew Salisbury, edited by Steve Head
Caterpillar of codling moth, Plum moth caterpillar in the core of a plum
Cydia pomonella Grapholita funebrana












